VISION
Fundamental research and application development
toward achieving carbon neutrality
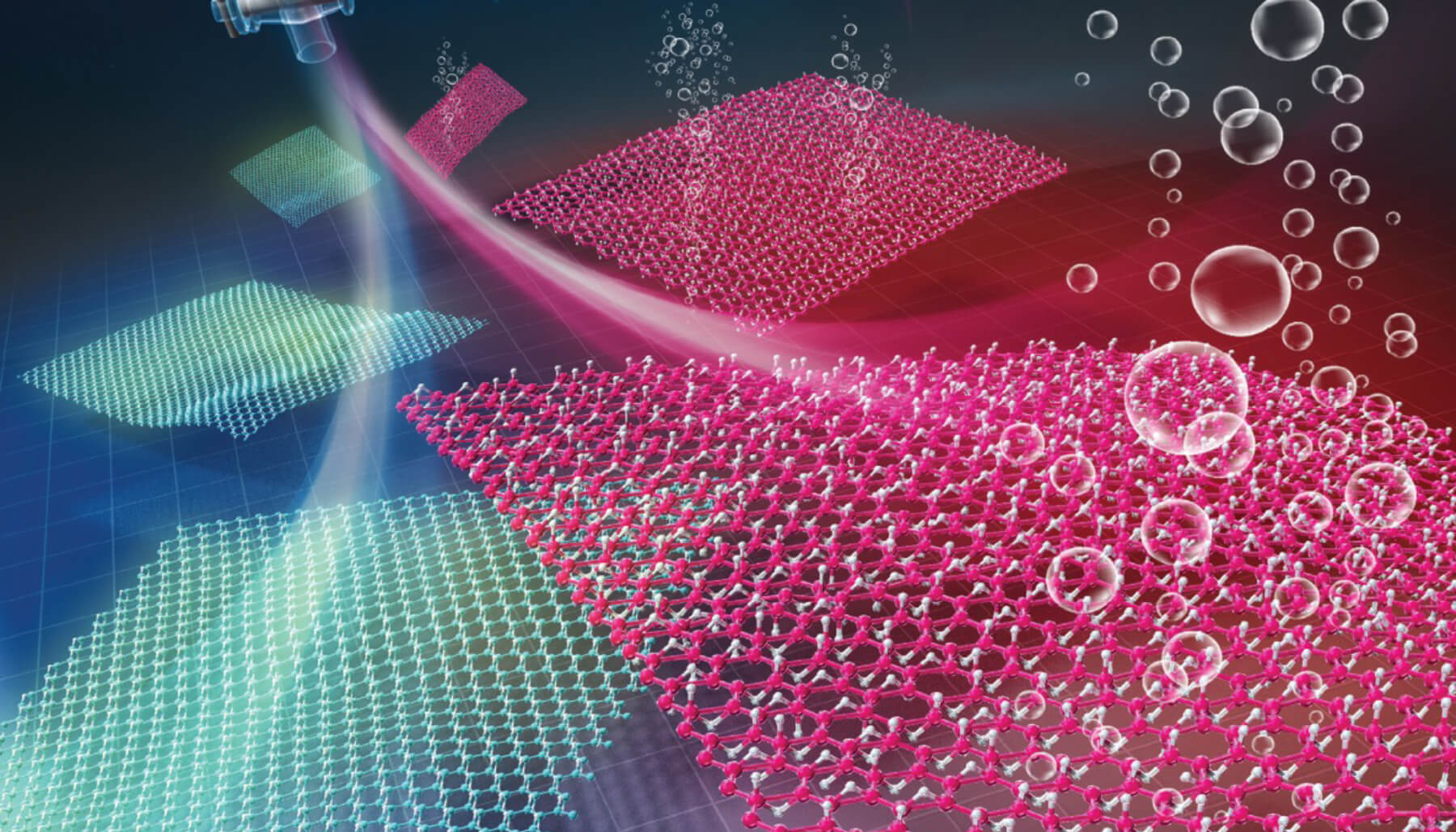
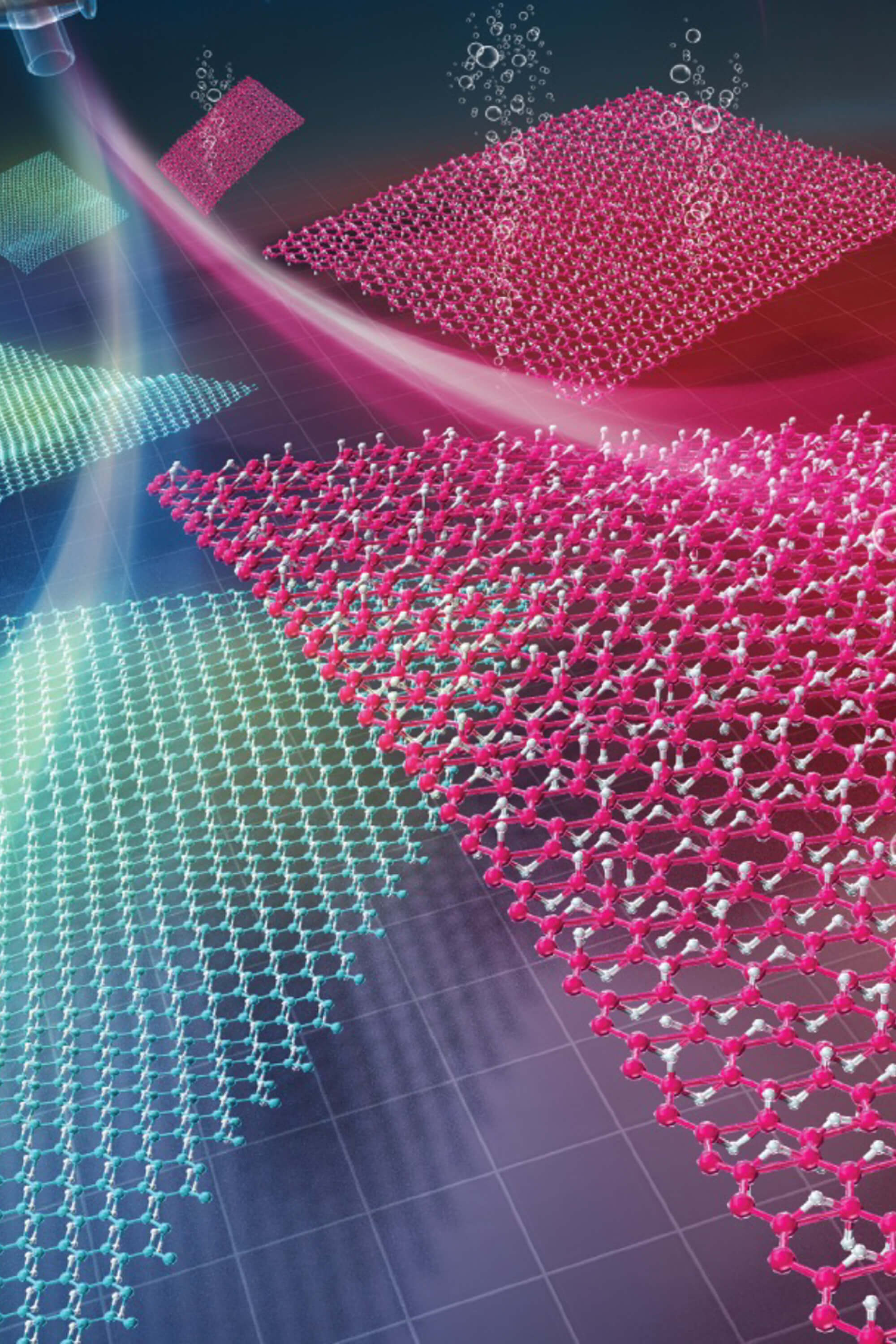
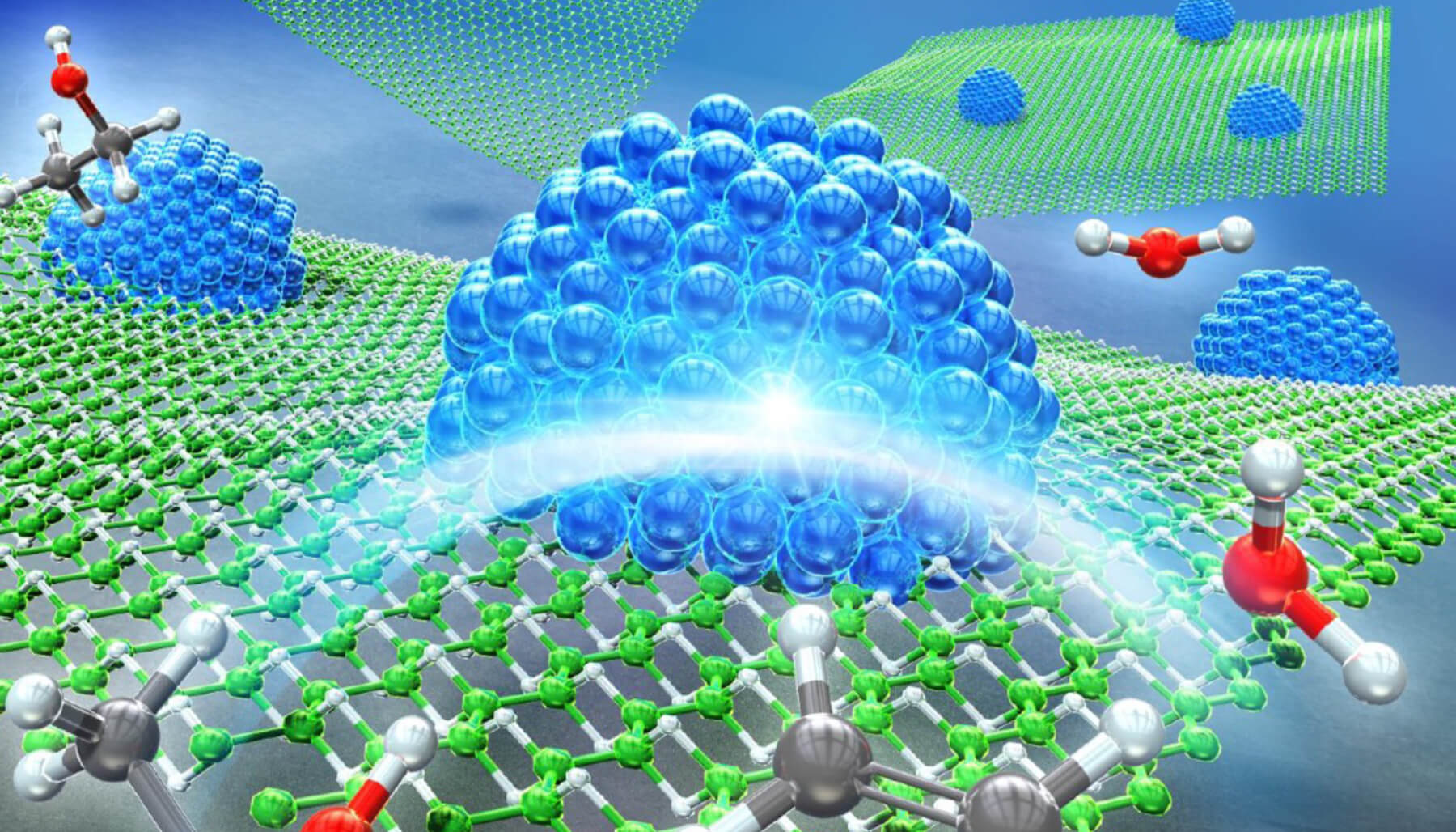
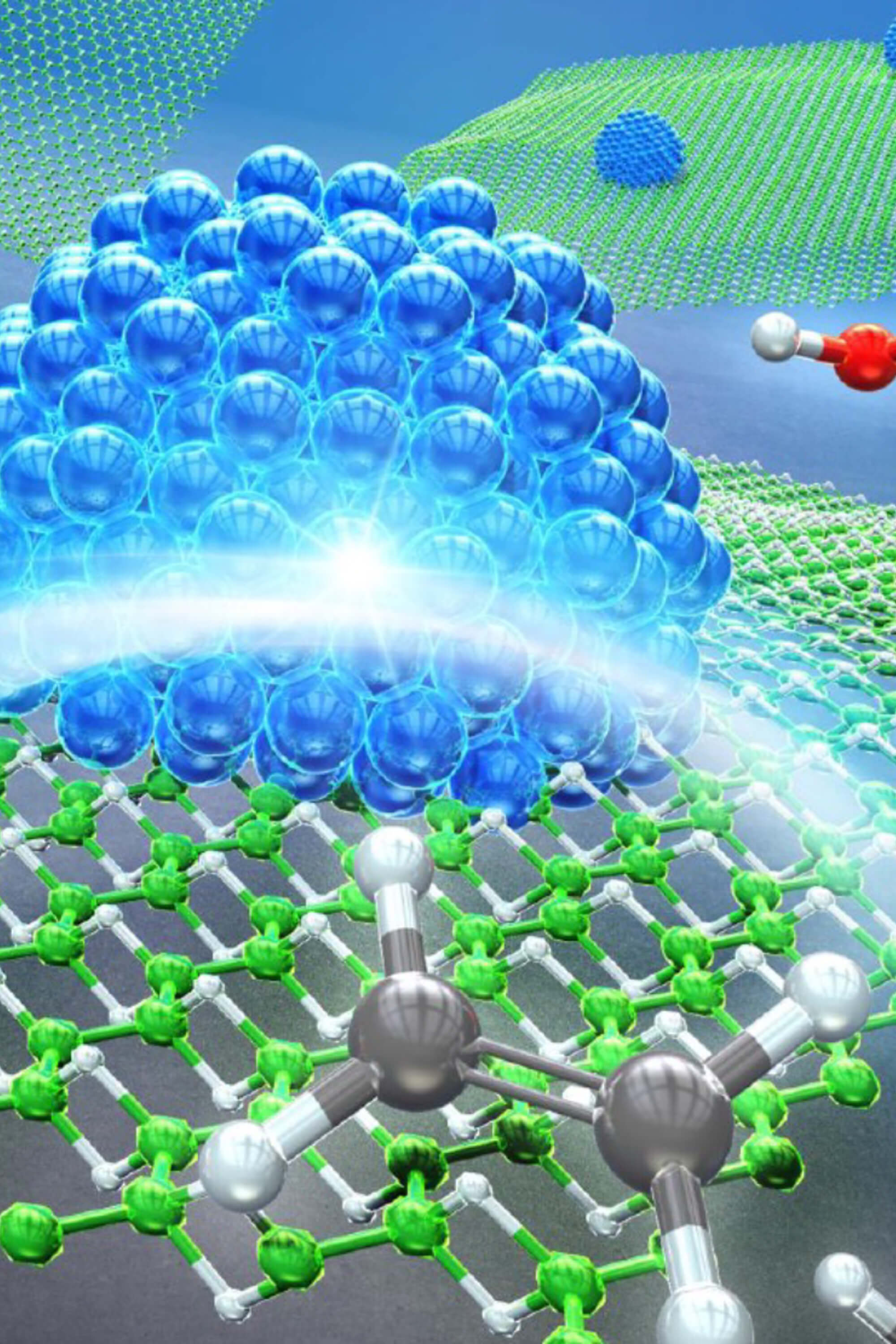
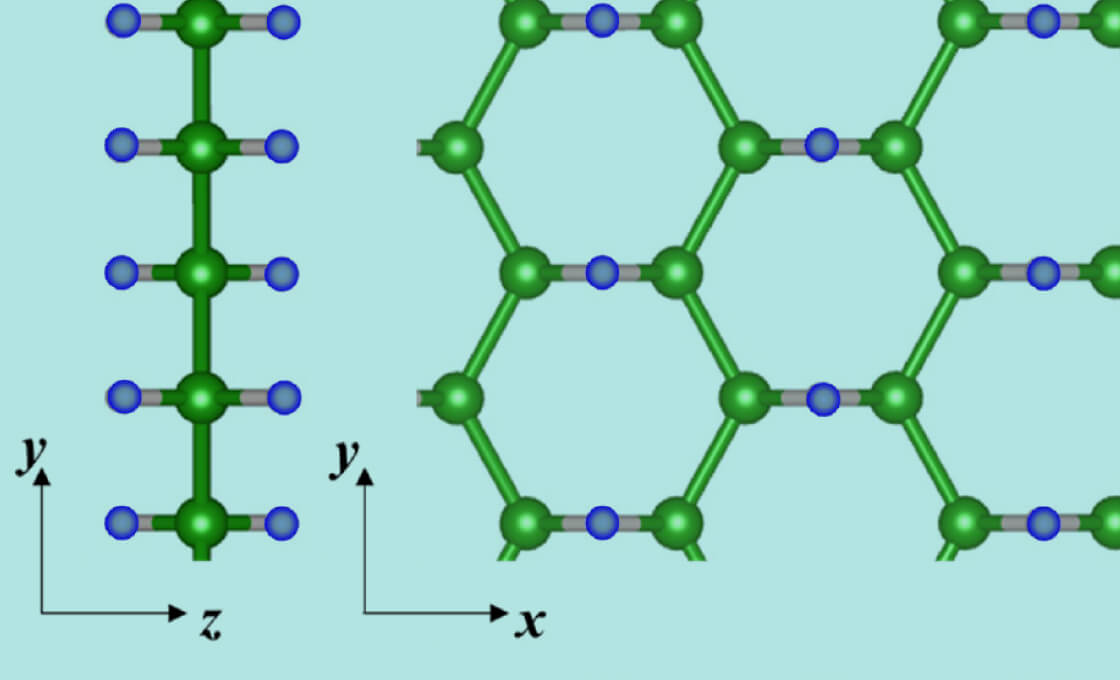
In 2017, researchers from the University of Tsukuba led the world's first successful synthesis of hydrogen boride (HB) nanosheets, a new two-dimensional nanosheets composed of lightweight boron and hydrogen (atomic ratio 1:1). Currently, applied research using HB is being carried out to solve various problems in the utilization of hydrogen, such as "producing, storing, transporting and usage". This center is the world's first base for such promising material, HB nanosheets. We will promote basic and applied research toward the realization of carbon neutrality.
News

- 2026.2.17
-
Research Results by Prof. Ito have been published at Chemical Engineering Journal!
Press release
Congratulations
-

- 2026.2.7
-
Collaboration Research results by Dogyun with Univ. Tokyo, Nagoya Univ. and Netherland has been published in Nuclear Fusion!
Plasma pulse induced dust release from tungsten co-deposited layer
Dogyun Hwangbo*, Shin Kajita, Sou Murakami, Yuki Hayashi, Hirohiko Tanaka and Thomas Morgan,
Nuclear Fusion 66 (2026) 034002.

- 2026.1.30
-
Please attend the following seminar!
Date: 2026/2/19 17:00
Location: Advanced Laboratory Building B310
Speaker: Dr. Michael T. Pettes
Affiliation: Deputy Group Leader and Staff Scientist, Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies, Los Alamos National Laboratory Title: Controlling Heat Conduction in Graphene and Carbon Nanomaterials by Strain and Isotope Engineering
Abstract: here
-

- 2026.1.9
-
Research paper about H2 release from L-HSi by Director Kondo, Dr. Oki, and other co-authors has been published at Advanced Optical Materials!
Press release
Visible-Light-Driven Hydrogen Release from Layered Hydrogen Silicane
Hirona Ito, Mio Nakai, Akira Yamaguchi, Shin-ichi Ito, Osamu Oki, Takahiro Kondo, Masahiro Miyauchi, Hideyuki Nakano
Advanced Optical Materials 14 (2026) e02880. (9 pages).

- 2025.12.12
-
Research paper about enhanced H2 release from HB nanosheets by Director Kondo, Dr. Oki, and other co-authors has been published at Small Structures
Enhanced Hydrogen Release from Hydrogen Boride Nanosheets via Carbon Doping
Riku Kawamura, Reiya Kawamura, Arpita Varadwaj*, Kazuaki Kisu, Rika Tanaka, Akiyasu Yamamoto, Ryota Ishibiki, Shin-ichi Ito, Takeshi Fujita, Tomoharu Tokunaga, Osamu Oki, Yoshitaka Fujimoto, Masayuki Toyoda, Susumu Saito, Toyoto Sato, Shin-ichi Orimo, Hideo Hosono, Iwao Matsuda, Masato Kotsugi, Masahiro Miyauchi*, Takahiro Kondo*
Small Structures 6 (2025) e202500578.

- 2025.12.10
-
Research paper about enhanced stability of HB nanosheets by Director Kondo, Prof. Ito, Dr. Oki, and other co-authors has been published at Small.
Enhanced Thermal- and Photostability of Trace Pyrazine-Incorporated Hydrogen Boride Nanosheets
Miwa Hikichi, Jumpei Takeshita, Junyan Han, Shin-ichi Ito, Osamu Oki, Ryuki Tsuji, Akira Hasegawa, Samuel Jeong, Yoshikazu Ito, Iwao Matsuda, Hayato Tsurugi, Masahiro Miyauchi, Takahiro Kondo*
Small 21 (2025) e06230.

- 2025.11.19
-
The joint research results by Prof. Kondo has been published at Scientific Reports!
Automated Elucidation of Crystal and Electronic Structures in Boron Nitride from X-ray Absorption Spectra Using Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection
R Hasegawa, A Varadwaj*, A L Foggiatto, M Niibe, T Yamazaki, M Horio, Y Ando, T Kondo, I Matsuda, M Kotsugi*
Scientific Reports 15 (2025) 37736.
Nature Publishing Group, Open Access
About
The logo of the Hydrogen Boride Research Center represents the transformation from a hexagon to a sphere in five stages, symbolizing the potential of hydrogen boride and the changes it will bring about in the future. The hexagon represents the structure of hydrogen boride, and the sphere represents the new future and applied technologies that will be born from that research.
Research
In 2017, researchers from the University of Tsukuba led the world's first successful synthesis of hydrogen boride (HB) nanosheets, a new two-dimensional nanosheets composed of lightweight boron and hydrogen (atomic ratio 1:1). Currently, applied research using HB is being carried out to solve various problems in the utilization of hydrogen, such as "producing, storing, transporting.